MBR (Membrane Bio-Reactor)
MBR (Membrane Bio-Reactor) can be broadly defined as systems integrating biological degradation of wastewater with membrane filtration.
Set up of MBR plant is mainly utilizing a bioreactor and membrane filtration as one unit process for wastewater treatment thereby replacing, and in some cases supplementing, the solids separation function of secondary clarification and effluent filtration, resulting the possibility to eliminate the secondary clarification and operate at higher MLSS concentration.
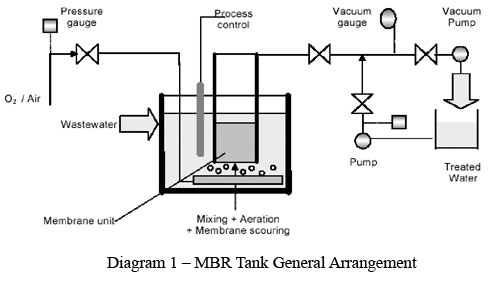
In summary, the MBR system is the combination of traditional Activated Sludge Treatment with the membrane technology. The design criteria of the system shall be base according to the traditional way of Activated Sludge Treatment principle. However, on top of that, the MBR modules are immersed and located in the air blow tank/ aeration basin (biological reactor tank), the clear water is pumped(sucked) out from the MBR modules. This shall possibly eliminate the needs of secondary clarifier. Refer Diagram 1.
Features of the MBR:
1 Better control of biological activity
2 Effluent that is free of bacteria and pathogens
3 Smaller foot print
4 Biodegradation efficiency enhanced 20%~40%
5 Short Hydraulic Residence Time (HRT) & Long Sludge Residence Time (SRT)
6 Activated sludge increase by 2~3 times
7 Higher organic loading rates
8 Adopt high strength polypropylene material membrane, easy cleaning, long lifespan to 5-7 years.
9 Convenient management with automatic control system.
How does it work:
1 Nos of pcs. of membrane are connected parallel through the header to form a frame. Connected frame
network will form a Membrane Unit.
2 It is then connected the suction side of a permeate pump, the membranes are subjected to a slight negative pressure of 10 to 30 kPa (1.5 to 4.5 psi).
3 In an “outside-in” process operation, water is drawn from the mixed liquor through the membrane module and into the hollow fiber, further enhanced by suction effect of pump. From there, the treated water is drawn through the header and out through the discharge system.
4 On a continuous basis, air is pumped into the bottom header, where it emerges as a fine bubble stream. This air stream performs the triple role of process aeration, mixing of the biomass and membrane cleaning. Refer Diagram 1.
5 Also, with the continuous movement of air bubbles around and through the fibers, a lower concentration of biomass is maintained around the membranes and this, in turn, minimizes the potential for membrane fouling.
6 The membrane module are modular design and can be dismantled individually for manual cleaning as part of supplementary periodic maintenance.

Forecasted Result:
The treated effluent would be used to irrigation, landscape, garden, car wash, toilet flush, etc.